Semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, is an incretin mimetic that has gained immense popularity for weight loss, marketed under names like Ozempic and Wegovy. But when it comes to using semaglutide for weight loss, understanding the dosage chart is critical. In this guide, we’ll explore why dosage matters, and how it can impact your journey toward achieving effective and sustainable weight loss.
The Basics of Semaglutide Dosage for Weight Loss
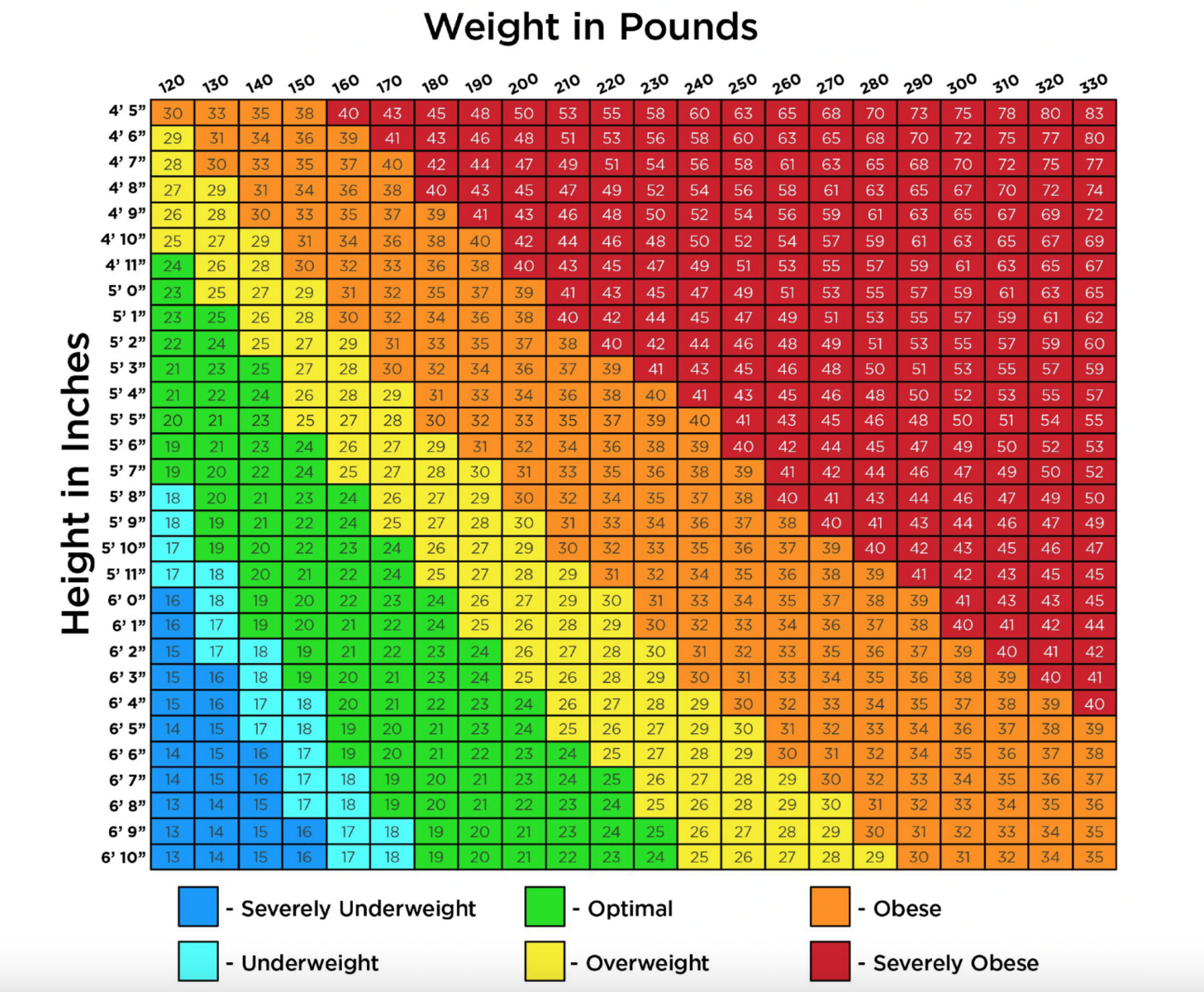
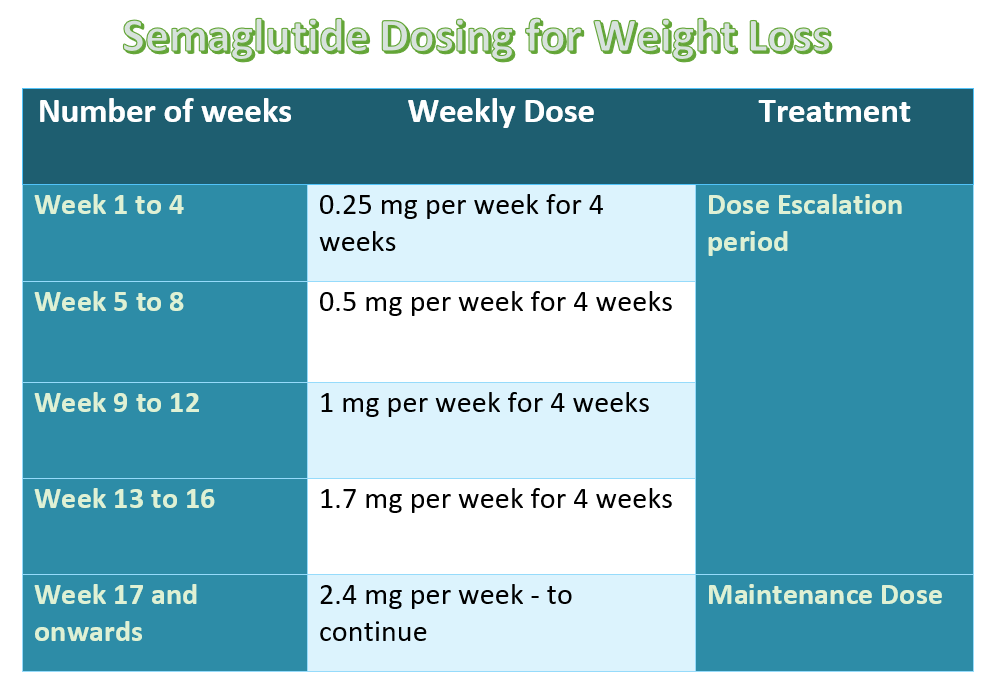
Let’s first break down the essentials of semaglutide dosage. Typically, semaglutide is administered as a subcutaneous injection. The weight loss dosage chart is designed to start patients at a lower dose to minimize side effects like nausea and vomiting, and gradually increase it to the most effective levels.
-
Week 1-4: Start with 0.25 mg weekly (This low dose helps the body adjust to semaglutide and reduces initial side effects.)
-
Week 5-8: Increase to 0.5 mg weekly
-
Week 9 and beyond: The standard maintenance dose is 1 mg weekly. However, some patients may require doses as high as 2.4 mg weekly, based on their weight loss progress and BMI.
Why the Right Dosage Is Crucial
Semaglutide dosage is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Factors like your starting weight, BMI, and overall metabolic health play a role in determining the optimal dose.
Impact of Dosage on Weight Loss:
-
Low Dosage (0.25 mg): Initial adjustment, limited weight loss effect but helps to minimize side effects like nausea and fatigue.
-
Medium Dosage (0.5 mg – 1 mg): This is where most patients see steady weight loss progress, improved insulin resistance, and a decrease in cardiovascular disease risk.
-
High Dosage (1 mg – 2.4 mg): Significant weight loss results, but also higher risk of side effects like hypoglycemia, constipation, and abdominal pain.
Infographic: Visualizing the Dosage Chart
Semaglutide Dosage Timeline and Weight Loss Effects
| Dosage (Weekly) | Low (0.25 mg) | Medium (0.5 mg – 1 mg) | High (1 mg – 2.4 mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weeks 1-4 | Initial Phase: Minimal weight loss. | Side effects begin to taper off. | Side effects manageable. |
| Weeks 5-8 | Titration: Gradual increase in weight loss. | Consistent weight loss begins. | Noticeable drop in body weight. |
| Weeks 9+ | Maintenance: Side effects reduced. | Moderate weight loss. | Optimal for most weight loss goals. |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When it comes to semaglutide weight loss, dosage adjustments must be made carefully. Here are some common errors that can hinder success:
A. Jumping to a High Dose Too Quickly
-
Starting at a higher dose (e.g., 1 mg or 2.4 mg) may seem like a faster way to lose weight, but it often results in severe side effects, leading patients to abandon treatment.
B. Skipping Weeks
-
Semaglutide should be administered weekly without skipping doses, as consistency ensures optimal regulation of your body’s insulin response.
C. Not Addressing Side Effects Early
-
Early side effects like diarrhea and constipation can often be managed by adjusting diet or activity levels. Ignoring these issues may make the treatment unsustainable.
How to Adjust Semaglutide Dosage Based on Results
Not everyone responds to semaglutide in the same way. You may need to adjust your dosage based on your weight loss progress.
Steps to Adjusting Your Semaglutide Dosage:
-
Monitor Side Effects: If you experience persistent nausea or vomiting, speak with your healthcare provider before increasing your dose.
-
Evaluate Weight Loss Progress: If after 8 weeks at 1 mg you have not experienced significant weight loss, your doctor may recommend increasing to 1.5 mg or 2 mg.
-
Watch for Plateaus: It’s common to hit a weight loss plateau. In these cases, a slight increase in dosage or changes in diet and exercise may help.
The Role of Semaglutide in Treating Obesity and Related Conditions
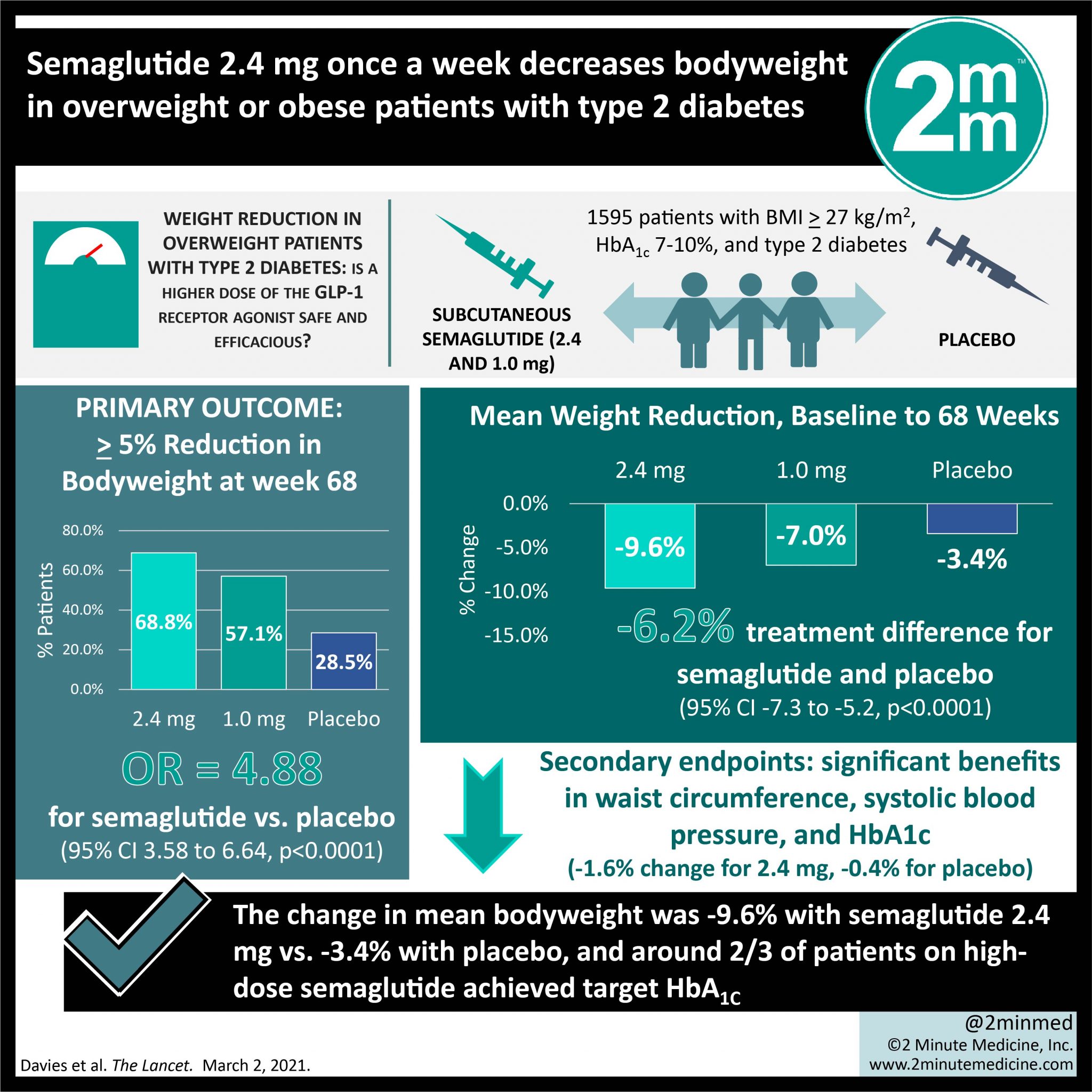
Semaglutide is not only effective for weight loss, but it also provides significant benefits for individuals suffering from obesity-related conditions like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The ability of semaglutide to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation makes it a key player in managing these conditions alongside weight loss.
Semaglutide Dosage and Lifestyle Adjustments
While semaglutide can be highly effective for weight loss, it’s crucial to pair the treatment with meaningful lifestyle changes for sustained results. Weight loss medications like semaglutide are most effective when combined with a calorie-controlled diet and regular physical activity. Here are some best practices for maximizing the effectiveness of semaglutide:
A. Diet Adjustments
-
Incorporate High-Protein Meals: High-protein meals not only keep you full but also support muscle retention during weight loss.
-
Manage Carbohydrate Intake: Focus on low-glycemic index carbs to improve insulin sensitivity and support weight loss.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drinking water can help minimize side effects like constipation and improve metabolic function.
B. Physical Activity
-
Start with Low-Intensity Exercise: For those new to exercise, begin with walking or swimming to ease into an active routine.
-
Strength Training: Building muscle can help increase your resting metabolic rate, which aids long-term weight maintenance.
-
Consistency Over Intensity: Aim for 150 minutes of moderate activity per week to complement the effects of semaglutide.
Side Effects: How to Manage and Minimize Them
Like any medication, semaglutide comes with potential side effects, especially as dosages increase. Most patients experience mild symptoms like nausea or diarrhea in the initial weeks of treatment, but there are ways to minimize these effects.
Low-Dosage Side Effects (0.25 mg – 0.5 mg)
-
Nausea: Eating smaller meals and avoiding high-fat foods can help manage nausea during the early stages of treatment.
-
Constipation: Increasing fiber intake and staying hydrated will help reduce the chances of constipation.
Medium-Dosage Side Effects (1 mg)
-
Fatigue: As your body adjusts to semaglutide, you might feel tired. Prioritize sleep and ensure you are not over-exerting yourself.
-
Diarrhea: This common side effect can often be managed by avoiding spicy and greasy foods.
High-Dosage Side Effects (1.5 mg – 2.4 mg)
-
Abdominal Pain: As dosages increase, some patients experience more intense abdominal discomfort. Staying consistent with injections and dietary habits can mitigate this.
-
Hypoglycemia: Though rare in non-diabetic patients, those on additional diabetes medications should closely monitor blood sugar levels to avoid low blood sugar episodes.
Semaglutide vs. Other Weight Loss Medications: How Does It Compare?
Semaglutide often gets compared to other weight loss medications like liraglutide (Saxenda) or exenatide (Byetta). Here’s a breakdown of how it compares in terms of dosage, effectiveness, and side effects:
Effectiveness Comparison
-
Semaglutide (1 mg – 2.4 mg): Proven to provide substantial weight loss, with many patients losing up to 15% of their body weight over the course of a year.
-
Liraglutide (0.6 mg – 3 mg): Offers moderate weight loss effects, typically around 5-8% body weight reduction.
-
Exenatide (2 mg weekly): Primarily used for type 2 diabetes, exenatide provides modest weight loss benefits, usually in the range of 3-5%.
Side Effects
-
Semaglutide: More effective at weight loss but has higher rates of nausea and vomiting, especially at higher doses.
-
Liraglutide: Mild side effects, with nausea being the most common.
-
Exenatide: Side effects similar to semaglutide but typically milder due to its lower weight loss potency.
Summary
Semaglutide weight loss dosage is a key factor in achieving effective and sustainable weight loss, with a dosage chart that allows for gradual adjustments based on individual progress and side effects. Starting with a lower dose, such as 0.25 mg weekly, and titrating up to 1 mg or higher can help patients lose weight while minimizing side effects like nausea or diarrhea. For those suffering from obesity, type 2 diabetes, or insulin resistance, semaglutide offers a promising solution that not only promotes weight loss but also provides additional health benefits.
To maximize the results of semaglutide treatment, it’s crucial to combine it with lifestyle changes like a balanced diet and regular exercise. Proper dosage adjustment based on side effects and weight loss progress ensures long-term success and can help avoid potential pitfalls like weight loss plateaus.
By understanding the semaglutide dosage chart and following best practices, individuals can safely and effectively reach their weight loss goals, improve metabolic health, and maintain their results over time.
FAQs: Your Questions Answered
1. What happens if I miss a dose of semaglutide? Missing a dose of semaglutide is not uncommon. However, if you miss your weekly injection, it’s important to administer it as soon as possible within 5 days. If more than 5 days have passed, skip the missed dose and resume your regular schedule.
2. Can semaglutide cause hypoglycemia? While hypoglycemia is a rare side effect for non-diabetic users, individuals with type 2 diabetes using semaglutide alongside insulin or other medications may experience low blood sugar levels. It’s important to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
3. How long does it take to see weight loss results with semaglutide? Most users begin to see noticeable weight loss after the first 4-8 weeks of treatment. Significant results are typically observed after 12 weeks, with the optimal dosage range being between 1 mg and 2.4 mg weekly.
4. Is semaglutide safe for long-term use? Semaglutide is approved for long-term weight management. However, long-term use may increase the risk of side effects such as gallbladder disease and pancreatitis. It’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to monitor your progress.
5. Can I stop taking semaglutide once I reach my weight loss goal? Stopping semaglutide abruptly may lead to weight regain. It’s important to maintain healthy lifestyle habits and consult your doctor on whether a reduced maintenance dose or continued use is recommended.
By understanding the semaglutide weight loss dosage chart